What is Virtualization?
In VMware’s own words, Virtualization is the process of creating a software-based (or virtual) representation of something rather than a physical one. Virtualization can apply to applications, servers, storage, and networks and is the single most effective way to reduce IT expenses while boosting efficiency and agility for all size businesses. VMware Virtualization is a technology that is used widely in the IT sector and if you are not familiar with it, let’s take a closer look.
Any Virtualization that is managed by a program is called a Hypervisor. A Hypervisor is basically a piece of computer software that creates and runs virtual machines. Generally, there are two types of Hypervisor technologies available, which are classified as follows:
1. Type-1 native or bare-metal Hypervisors
2. Type-2 or hosted Hypervisors.
The Type-1 is a Virtualization technology which provides direct interaction to the hardware without help of any operating system and hence are directly run on the host’s hardware to control the hardware and to manage guest operating systems.
In case of Type-2, it requires an Operating System in order to interact with the hardware. Here Hypervisor is installed along with the OS.
VMware workstation, VMware player etc come under Type-2 Virtualization and among the two, the most commonly used VMware Virtualization is the Type-1 Hypervisor in the case of a production environment.
As mentioned earlier, Type-1 Hypervisor does not require an OS to communicate with the hardware and to perform necessary functions. VMware ESXi Hypervisor is used instead which is a Type-1 Hypervisor developed by VMware for deploying and serving virtual computers that includes all necessary components including its own Kernel. In short, ESXi is an OS developed by VMware to interact with hardware and perform functions.
Now vSphere, previously known as VMware Infrastructures a software suite, as in, a collection of several softwares such as vCenter, ESXi, vSphere Client.
You do not have direct access to ESXi. ESXi is a Virtualization server of type 1 hypervisor and you will need an additional system to connect/configure to it such as vCenter or vSphere client.
Both vCenter and vSphere client are similar in basic use but differ in their possibilities with vCenter being the more advanced one. Even though the vSphere client does a great job in managing smaller environments, it cannot be used to perform all the actions in ESXi. Users don’t always need vCenter and can get away with using a vSphere client in most scenarios especially when you consider the high licensing cost of vCenter
However, when you are managing a larger environment and require much advanced features, here is where vCenter comes in. vCenter acts like a server which is installed on top of a Windows VM and a Windows VM runs on top of ESXi host.
Refer Img:
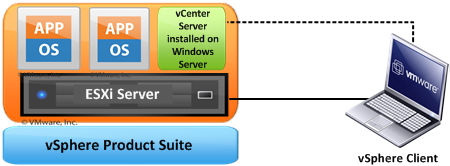
The advanced features you get from using vCenter are listed below:
- vMotion
- HA (High Availability)
- DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler)
vMotion allows us the possibility running maintenance without downtime. This mechanism keeps the networks and connections up and ensures a stable migration. This means we can to transfer one virtual machine from one physical sever to another server with
The migration process will consume only minimal time in comparison with other types of migrations.
With HA present, the downtime of a complete server is minimized with the ability to restart the VM automatically on another host. However, it does not monitor any independent services within the server.
DRS is used to automatically balance the resources in the VM according to the work load. This function optimizes the resources without interruption of any services and helps to reduce the power consumption which helps to reduce the operational cost. As DRS balances the resources, we can add more resources without any service interruptions or technical failures.
To put it in a nutshell, VMware is a visualization server which is a combination of hardware, ESXi, vSphere, vCenter and so on. At the end, VMware is more convenient to use and is more effective than any other Virtualization software in the present IT era.
About the Author:
Alan is passionate about open-source projects as much as he in his sports. A dedicated, self motivated and solution-minded team player who claims to have a rare knack of grasping things very quickly and coming up to speed in a very short period of time.







Nicely written.
Thank you for this informative article